Trichosporon: Introduction,pathogenecity, lab diagnosis and treatment
Introduction of Trichosporon
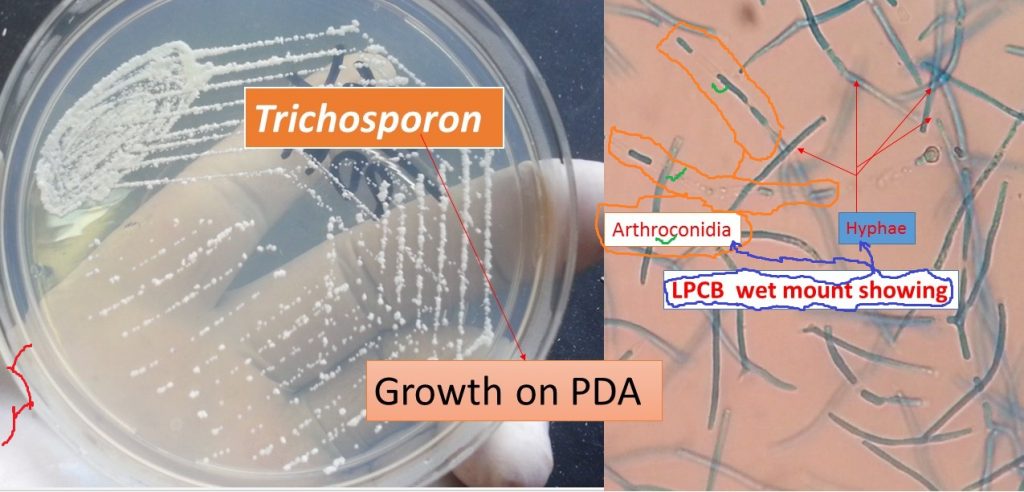
The fungus Trichosporon (genus) is characterized by the development of structures like hyaline, septate hyphae that fragment into oval or rectangular arthroconidia. The colony characteristics are suggestive for the usually raised colony and have a waxy appearance, which develops radial furrows and irregular folds.
Pathogenicity of Trichosporon
6 species of medical importance are listed below-
- Trichosporon asahii
- Trichosporon asteroides
- Trichosporon cutaneum
- Trichosporon inkin
- T. mucoides and
- T. ovoides.
They are a minor component of normal skin flora and are widely distributed in nature. They are regularly associated with the soft nodules of white piedra and have been involved in a variety of opportunistic infections in an immunosuppressed patients.
Disseminated infections are most frequently caused by T. asahii and have been associated with the following conditions like leukemia,
organ transplantation
multiple myeloma
aplastic anemia
lymphoma
solid tumors and
AIDS.
Disseminated infections are often fulminated and widespread, with lesions occurring in the liver, spleen, lung, and gastrointestinal tract.
Infections in non-immunosuppressed patients include endophthalmitis after surgical extraction of cataracts, endocarditis usually following insertions of prosthetic cardiac valves, peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD), and intravenous drug abuse.
Risk group
They come under risk group-2 organisms.
Laboratory diagnosis of Trichosporon
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation
- Culture of the specimen into Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) or Potato dextrose agar (PDA)
- Lactophenol cotton blue (LPCB) tease mount
- Assimilations tests using a variety of sugars like glucose, galactose, sucrose, maltose, cellobiose, trehalose, and so on
Key to medically important species
Arthroconidia barrel-shaped; thallus, not meristematic –T. asahii
Arthroconidia elongate, or thallus meristematic –T. asteroides
Not tolerant to cycloheximide – T. cutaneum
Growth with Myo-inositol, no growth with L-arabinose – T. inkin
Tolerant to cycloheximide –T. mucoides
Appressoria present in slide culture – T. ovoides
Treatment
Following anti-fungal drugs use for treatment these etiological agents and they are-
- Fluconazole
- Itraconazole
- Posaconazole
- Voriconazole
- Amphotericin B
- Flucytosine
- Caspofungin
- Anidulafungin
but anti-fungal susceptibility may vary between species and resistant strains have been reported. Therefore, antifungal susceptibility testing of individual strains is recommended.
Further Reading
- Collier L, Balows A, Sussman M. Topley, and Wilson’s Microbiology and MIcrobial infections. 9th Edition.Mycology Volume 4
- Jagdish Chander. A textbook of Medical Mycology.
- Description of Medical Fungi-David Ellis, Stephen Davis, Helen Alexiou, Rosemary Handke, Robyn Bartley
