Staphylococcus Versus Micrococcus : Introduction and Application in Details
Introduction of Staphylococcus Versus Micrococcus
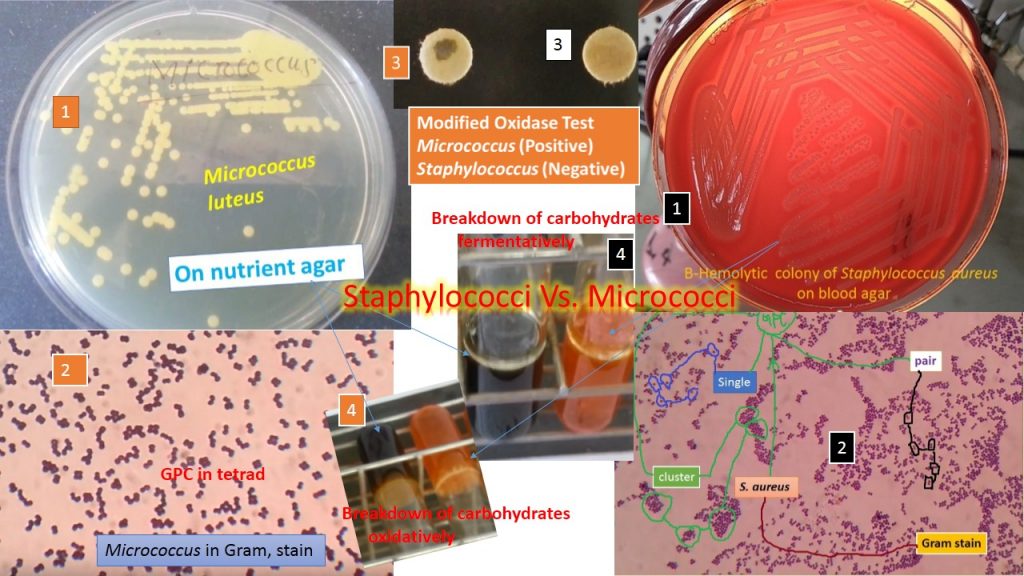
Distinguishing features of Staphylococcus versus Micrococcus (pleural-micrococci) can easily understand. Staphylococcus (pleural-staphylococci) is Spherical, non-motile, gram-positive, cluster forming. On nutrient agar, growth is opaque and golden yellow or white color. Catalase test positive, coagulase test positive (Staphylococcus aureus), oxidase negative, aerobic or facultative anaerobe. Parasite of humans and animals. Normal flora of the skin, upper respiratory tract, and feces of humans, animals, and birds too. Species of Staphylococcus are-
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus schleriferi
- Staphylococcus felis
- Staphylococcus intermedius
- Staphylococcus lutrae
- Staphylococcus hyicus
- Staphylococcus lodgunensis
- Staphylococcus lodgunensis
- Staphylococcus schleriferi
- Staphylococcus hyicus
Micrococcus is free-living in the environment. It is Gram-positive cocci, catalase-positive, coagulase-negative, arranged in clusters that differ from Staphylococcus in attacking sugars oxidatively. It may appear in irregular clusters, groups of four or eight. It is often larger than Staphylococcus. Species of Micrococcus are-
- Micrococcus luteus
- Micrococcus lylae
- Micrococcus terreus
- Micrococcus mortus
- Micrococcus mucilaginosis
- Micrococcus roseus
The differences between Staphylococcus and Micrococcus are on the basis of the following features-
- Anaerobic growth
- Arrangement of cells (predominant)
- Mol % G+C of DNA
- Carbohydrate utilization
- Oxidase (modified oxidase test)
- 0.04U bacitracin
- Lysostaphin
- Teichoic acid in cell wall
Staphylococcus versus Micrococcus
| Property | Staphylococcus | Micrococcus |
| Anaerobic growth | positive | Negative |
| Arrangement of cells (predominant) | Clusters | Clusters, tetrads |
| Mol % G+C of DNA | 30-39 | 64-75 |
| Carbohydrate utilization | Fermentative | Oxidative or nil |
| Oxidase (modified oxidase test) | Negative | Positive |
| 0.04U bacitracin | Resistant | Sensitive |
| Lysostaphin | Sensitive | Resistant |
| Teichoic acid in cell wall | Present | Absent |
Further Readings
- Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology. Editors: Bettey A. Forbes, Daniel F. Sahm & Alice S. Weissfeld, 12th ed 2007, Publisher Elsevier.
- Clinical Microbiology Procedure Handbook Vol. I & II, Chief in editor H.D. Isenberg, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, Publisher ASM (American Society for Microbiology), Washington DC.
- Colour Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology. Editors: Koneman E.W., Allen D.D., Dowell V.R. Jr, and Sommers H.M.
- Cowan & Steel’s Manual for identification of Medical Bacteria. Editors: G.I. Barron & R.K. Felthani, 3rd ed 1993, Publisher Cambridge University Press.
- Jawetz, Melnick and Adelberg’s Medical Microbiology. Editors: Geo. F. Brook, Janet S. Butel & Stephen A. Morse, 21st ed 1998, Publisher Appleton & Lance, Co Stamford Connecticut.
- Mackie and Mc Cartney Practical Medical Microbiology. Editors: J.G. Colle, A.G. Fraser, B.P. Marmion, A. Simmous, 4th ed, Publisher Churchill Living Stone, New York, Melborne, Sans Franscisco 1996.
- Manual of Clinical Microbiology. Editors: P.R. Murray, E. J. Baron, M. A. Pfaller, F. C. Tenover and R. H. Yolken, 7th ed 2005, Publisher ASM, USA
- Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology. Editors: Connie R. Mahon, Donald G. Lehman & George Manuselis, 3rd edition2007, Publisher Elsevier.
- Topley & Wilsons Principle of Bacteriology, Virology, and immunology Vol I, II, III, IV & V. Editors: M.T. Parker & L.H. Collier, 8th ed 1990, Publisher Edward Arnold publication, London.
- Medical Microbiology-The Practice of Medical Microbiology Vol-2-12th Edn. –Robert Cruickshank
- District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries – Part-2- Monica Cheesebrough- 2nd Edn Update
