Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Introduction, Pathogenicity, Lab Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction of Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a common respiratory virus that normally causes mild, cold-like symptoms. Most of the sufferers recover in a week or two, but RSV can be serious, particularly for infants and older adults. Some features of this virus are-
- belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae
- Enveloped RNA virus
- Pleomorphic with helical capsid symmetry
- 90-130 nm in size
Transmission and pathogenicity of RSV
Person to person transmission is mainly by droplet infection. It can also spread direct contact with the virus, like kissing the face of a child with RSV and touching a surface that has the virus on it, like a doorknob, and then touch. Disease-Server bronchiolitis and pneumonia in infants and small children. Othe clinical condition are upper respiratory tract infection and otitis media as a complication in young children.
Symptoms of RSV
The expression of symptoms only comes within 4 to 6 days after getting infected. The symptoms of this infection usually include-
- Runny nose
- Coughing
- Decrease in appetite
- Sneezing
- Fever
- Wheezing
Laboratory Diagnosis of Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Specimen: The following specimens are appropriate –
- Throat swab
- Nasal swab
- Nasopharyngeal aspirate
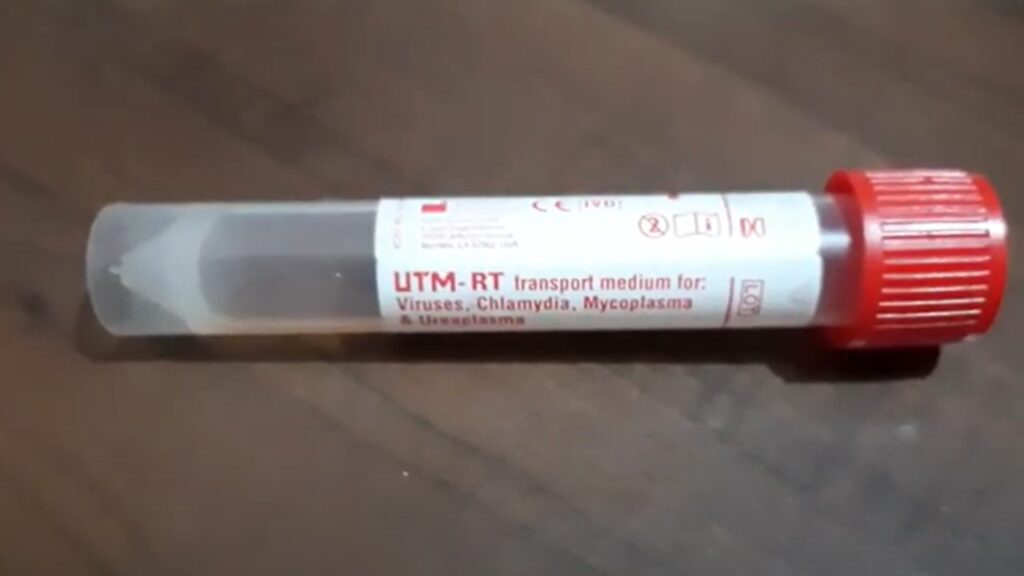
Transport medium: Collect specimen into viral transport medium and frozen immediately at -70 °C.
Serological assays-
- Direct demonstration of antigen
- Direct immunofluorescence test
- ELISA
- Immunoperoxidase test
Nucleic acid and technology: PCR
Culture : Isolation of the virus from nasopharyngeal aspiration is difficult because it remains an infection only for short time.
Tissue culture: Hep-2 cell lines, HeLa cells
Cytopathic effect on the cell: Infected cells joined together thus called syncytia
Inclusion bodies may be present.
Treatment
Most infections go away on their own within 7-14 days and there is no specific treatment for infection. Vaccine: No effective vaccine available so far against this virus hough researchers are working to develop vaccines. It is beleived that breastfeeding provides some protection to infants.
Keynotes on RSV
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
- Bronchitis is an inflammation of the small airways in the lung.
- Coughs and sneezes should be covered with a tissue or upper shirt sleeve, but not hands.
Further Reading
- https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/about/symptoms.
- htmlhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3461981/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/respiratory-syncytial-virus/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353104
- https://openmicrobiologyjournal.com/VOLUME/5/PAGE/128/FULLTEXT/
